Precision Sheet Metal Parts: Applications and Advantages
These parts as per the manufacturer of precision-machined components in India are normally produced by advanced equipment such as CNC machines, laser cutting, and program-controlled brake presses.
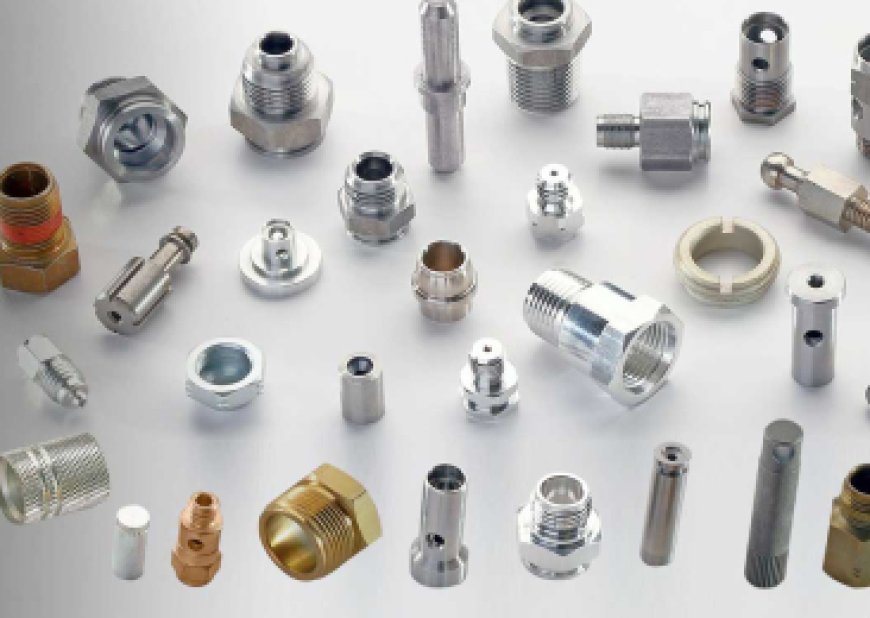

With the era of rapid manufacturing, precision and accuracy are requirements and not desires. Precision sheet metal fabrication is one of the world's leading participants in this revolution. Precision sheet metal parts are the backbone that guarantees performance, reliability, and competitiveness in consumer electronic devices, aerospace components, and extremely intricate medical devices.
Here in this blog, we define what precision sheet metal parts are, their extensive applications, and how life today is enriched by industries with them.
What are Precision Sheet Metal Parts?
Precision sheet metal components are pieces that are manufactured by extremely precise cutting, bending, punching, and assembly of sheet metals (aluminium, stainless steel, brass, or copper) into precise forms. "Precision" is what is described by tight tolerances developed—typically by fractions of a millimetre—so that it is highly repeatable and trustworthy.
These parts as per the Manufacturer of Precision Machined Components in India are normally produced by advanced equipment such as CNC machines, laser cutting, and program-controlled brake presses. In addition, with the use of technologies such as 3D CAD modelling and CAM integration, the manufacturers are able to offer error-free manufacturing from design through delivery.
Most Popular Applications of Precision Sheet Metal Components
Precise sheet metal components have invaded almost all of the heavy industries in massive quantities. Their scalability in both directions has set them as the standard in today's industrial trade. Let us look into their most common uses in closer detail:
1. Electronics Industry
Accurate sheet metal components perform significant roles in the production of equipment electronics' protection enclosures and brackets. Think about your smartphone stand or your computer cover. Such components need to be small, heatproof, and heavy-duty.
Examples: Server racks, battery boxes, EMI/RFI shielding, and terminal boxes.
2. Automobile Industry
From motor vehicle engine parts to electric vehicle battery cases, precision sheet metal provides motor vehicles with lightness, stability, and defence.
Examples: Heat shields, EV battery trays, dashboard frames, and brackets.
3. Aerospace & Defense
Lightness is the lifeblood of the aerospace industry. Sheet metal parts provide strength without the cost of weight, a necessity for parts that must endure extreme conditions and stress.
Examples: Aircraft skin panels, turbine housing, missile compartments, and control boxes.
4. Medical Devices
Medical applications require clean, good-quality, and durable components. Precise sheet metal enables the creation of durable yet complex components for diagnostic equipment and surgical instruments.
Examples: Equipment enclosures, surgical tray sets, and monitor mounts.
5. Telecommunications
Telecommunication devices depend on excellent sheet metal enclosures for base stations, switches, and servers. They are secure, well-ventilated, and easy to access.
Examples: Amplifier enclosures, network enclosures, and antenna mounts.
6. Industrial Machinery
Accurate sheet metal parts are also applied in manufacturing machines, automation systems, and control panels because of their hardness as well as ease of maintenance.
Examples: Control panels, mounting plates, conveyor system parts, and machine guards.
7. Consumer Products
Accurate sheet metal parts have their way into every type of consumer product—high-tech kitchen appliance or home gym equipment.
Examples: Air conditioner panels, ergonomic support, and oven interiors.
Advantages of Precision Sheet Metal Products
Precision sheet metal offers a broad overall range of advantages over cast or conventional parts and is thus the industry norm for scalability, precision, and dependability for use.
1. High Repeatability and Accuracy
Precise manufacturing ensures every piece is to the precise specifications with no variation. This is particularly imperative in fields such as aerospace or medicine, where a slight variation can have disastrous implications.
2. Design Flexibility
New manufacturing methods allow engineers to produce intricate geometry with low variation in tooling. If you need one prototype or production runs, sheet metal provides design flexibility that's hard to beat.
3. Light but Strong
Application of thin yet light material such as aluminium or titanium allows one to minimize the weight of the product without minimizing structural strength. It is ideal for transport-oriented products such as automotive or aerospace.
4. Economical Production
Sheet metal fabrication is economical for medium- to high-volume production. Processes such as nesting (optimization of sheet layout) minimize scrap, and CNC machines allow production cycles to be efficient.
5. Fast Turnaround
With CAD/CAM integration technology and automated software, designers can go straight from design to production in very short time frames—ideal for time-consuming applications.
6. Corrosion Resistance and Surface Finish Opportunities
Materials like stainless steel have built-in corrosion resistance, and coatings like powder coating, anodizing, or plating have hardness and form.
7. Easy Assembly and Integration
Precision sheet metal components are generally made to fit together. Tabs, slots, and countersink holes can be incorporated in the product so that no secondary processes are required.
Technologies Used in Precision Sheet Metal Fabrication
Precision is where talent meets technology. Some of the technologies used here are the following:
Laser Cutting:
Accurately cuts with high-powered lasers and minimal heat distortion, most suitable for close tolerance and precision detail work.
● CNC Punching: Punches huge numbers of holes very efficiently, particularly forms or louvres, very effectively. It is used primarily to operate on ventilation panels or mounting plates.
● Press Braking: For sheet metal forming into fixed angles. Sophisticated brake presses employ digital angle control for precision.
● Welding & Fastening: TIG, MIG, spot welding, and rivets are common joining methods. Accuracy welding is used to provide structural integrity and finish.
● Finish: Deburring, sanding, and coating processes give a finished product that can be utilized or assembled with little rework.
Conclusion
Precision sheet metal parts are the unsung workhorses behind so much technology today. From household consumer goods to the aerospace sector, precision sheet metal components make things work, perform, and live longer.
As businesses work to do more in less time, smarter, and greener, precision sheet metal will be the underlying technology—pliant enough for accelerated design change and durable enough for more life. As a product engineer, designer, or OEM manufacturer, knowing the variety and value of precision sheet metal components can help you make smart decisions and stay competitive.